The Gut Brain Connection: Exploring How Gut Health Impacts Mental Wellness
Bloom Health and Wellness
Exploring How Gut Health Impacts Mental Wellness
Recently, there has been a growing appreciation for the intricate relationship between our gut and brain. This connection, often called the "gut-brain axis," is a complex and bidirectional communication system that plays a pivotal role in our overall well-being. Surprisingly, the state of your gut health can profoundly impact your mental wellness. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the gut-brain connection, exploring how gut health influences mental health and what you can do to nurture both.
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Symbiotic Relationship
The gut-brain axis is a dynamic communication network between the central nervous system (your brain and spinal cord) and the enteric nervous system (the intrinsic nervous system of your gut). This connection is facilitated by a complex web of neurons, hormones, and signaling molecules that allow the two systems to communicate seamlessly.
1. The Vagus Nerve: One of the primary conduits for this communication is the vagus nerve, a long cranial nerve that extends from the brainstem to the abdomen. The vagus nerve transmits signals in both directions, allowing the gut to send information to the brain and vice versa.
2. Microbiota: At the heart of this interaction lies the gut microbiota, a diverse community of trillions of microorganisms living in your digestive tract. This microbial population plays a crucial role in maintaining a balanced gut-brain axis.
Gut Health and Mental Wellness: A Two-Way Street
Now, let's explore how gut health can impact mental wellness and vice versa:
Mood and Emotions
Research has revealed that the gut microbiota can influence your mood and emotions. The gut produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, often referred to as the "feel-good" hormone, which plays a pivotal role in regulating mood. Approximately 90% of serotonin is produced in the gut, making a healthy gut microbiome essential for maintaining a positive mood.
Conversely, chronic stress and mood disorders like anxiety and depression can negatively impact gut health. Stress can alter the composition of the gut microbiota, potentially leading to gastrointestinal issues and a compromised gut-brain axis.
Inflammation and Immunity
A well-balanced gut microbiome helps regulate inflammation throughout the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to various physical ailments and contributes to mood disorders and cognitive decline. A healthy gut can help reduce systemic inflammation, which, in turn, benefits mental wellness.
Conversely, chronic stress and poor mental health can trigger inflammation in the body, disrupting the gut's delicate balance. This inflammation can further impair the gut-brain axis, potentially worsening mental health symptoms.
Brain Function and Cognitive Health
Emerging research suggests that the gut microbiome plays a role in cognitive function and brain health. An imbalanced gut microbiota has been associated with conditions like Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Additionally, the gut-brain axis may impact cognitive functions like memory and decision-making.
On the flip side, mental exercises, such as engaging in cognitive activities and staying mentally active, can positively influence the gut-brain axis by promoting a healthier gut microbiota.
Stress and Anxiety
Stress, particularly chronic stress, can disrupt the gut-brain axis and contribute to gastrointestinal issues. This connection is often referred to as the "brain-gut axis," as stress signals from the brain can affect gut function and vice versa.
Chronic stress can lead to changes in gut motility, increased inflammation, and alterations in the gut microbiota composition, all of which can exacerbate anxiety and other mental health conditions.
Nurturing Your Gut and Your Mind
Understanding the intricate relationship between gut health and mental wellness underscores the importance of caring for both. Here are some practical steps you can take to nurture your gut and promote better mental health:
1. Eat a Diverse Diet
Aim for a varied and balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi. These foods can help promote a healthy gut microbiome.
2. Probiotics and Prebiotics
Consider incorporating probiotics (live beneficial bacteria) and prebiotics (fiber-rich foods that feed beneficial bacteria) into your diet. Probiotic supplements and foods like kefir and sauerkraut can help maintain a healthy gut microbiota.
3. Manage Stress
Practice stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or mindfulness to reduce the impact of chronic stress on your gut and mental health.
4. Regular Exercise
Physical activity has been shown to positively influence both gut health and mental wellness. Aim for regular exercise to support a healthy gut-brain axis.
5. Prioritize Sleep
Aim for quality sleep by establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a conducive sleep environment. Sleep is essential for both gut repair and mental rejuvenation.
6. Seek Professional Help
If you're experiencing chronic gastrointestinal issues or mental health concerns, don't hesitate to seek professional help. A healthcare provider or mental health specialist can offer guidance and treatment options tailored to your needs.
7. Limit Processed Foods
Reduce your intake of processed foods, added sugars, and artificial additives, as they can negatively impact gut health and exacerbate mental health symptoms.
8. Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support digestive processes and overall well-being.
9. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as these habits can harm both gut and mental health.
10. Foster Social Connections
Nurture your social relationships and seek emotional support from friends and family, as social connections are essential for mental wellness.
The gut-brain connection is a fascinating and intricate relationship that underscores the importance of holistic health. By taking steps to support your gut health through diet, stress management, and lifestyle choices, you can positively impact your mental wellness. Similarly, prioritizing mental health through stress reduction and emotional support can contribute to a healthier gut-brain axis. Remember that these efforts are not isolated but work together to create a harmonious balance between your gut and your mind, ultimately promoting a happier and healthier you.

As healthcare costs continue to rise and patients struggle to get the care they need, more people are looking for a better way to access medical services—one that’s transparent, affordable, and centered on them. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we believe Direct Primary Care (DPC) is the future of healthcare in America, offering a refreshing alternative to the traditional insurance-based system. The Current State of Healthcare It’s no secret that the U.S. healthcare system is complicated and costly. Even with insurance, many people face: High monthly premiums Large deductibles before coverage even begins Long wait times for appointments Rushed visits with limited face-to-face time Surprise bills after routine care The result? Patients often avoid seeing their provider altogether—until a small issue becomes a major health concern. This traditional model of healthcare isn’t working for most people. But the good news is, there’s a better way. What Is Direct Primary Care? Direct Primary Care (DPC) is a modern approach to healthcare that eliminates the middleman—insurance companies—and puts the focus back where it belongs: on the patient-provider relationship. For a low monthly membership fee, patients receive: Unlimited access to their provider Same-day or next-day appointments Longer, more personalized visits Direct communication by phone, text, or email Transparent pricing with no surprise bills At Bloom Health and Wellness, our DPC model allows patients to get the care they need—when they need it—without the stress of insurance hurdles or unexpected expenses. Why Direct Primary Care Costs Less It may sound too good to be true, but DPC can actually help **save money** in the long run. Here’s how: 1. No Insurance Middleman Because DPC operates outside of traditional insurance billing, we remove unnecessary administrative costs. This allows us to keep membership fees low and focus on providing care instead of paperwork. 2. Preventive and Proactive Care In a traditional system, care is often reactive—patients wait until something is wrong. DPC makes it easier to stay proactive with regular check-ins, lifestyle guidance, and early intervention, helping to prevent costly emergency visits or hospital stays. 3. Transparent, Predictable Pricing Our patients know exactly what they’ll pay each month—no surprise bills or confusing statements. That predictability makes it easier to budget for healthcare. 4. Reduced Need for Expensive Specialist Visits Because DPC providers have more time with each patient, many issues that would normally require a referral can be handled in-office, saving time and money. 5. Wholesale Lab and Medication Costs Many DPC practices offer deeply discounted rates on labs and procedures. These savings add up quickly—especially for families. The Changing Landscape of Healthcare The healthcare landscape in America is shifting. More patients want **convenience, connection, and clarity**, and more providers are choosing to step away from insurance-heavy systems that limit their ability to truly care for patients. Direct Primary Care aligns perfectly with these changes—it’s personal, transparent, and flexible. It restores the relationship between patient and provider while providing a sustainable model for the future. Why Patients Love the DPC Model Our members at Bloom Health and Wellness consistently tell us how much they value: Quick access to their provider when something feels off Longer appointments where they feel heard and not rushed Affordable care they can actually understand and plan for A true partnership in achieving better health and wellness Instead of being a number in a system, you become a valued member of a health partnership built around your unique needs. Direct Primary Care and the Future of Wellness At Bloom Health and Wellness, we see Direct Primary Care as more than just a new way to access medical care—it’s part of a larger movement toward preventive, whole-body wellness. By spending more time with each patient, we can focus on the root causes of symptoms, address lifestyle factors, and provide ongoing guidance that supports long-term health. When patients feel empowered and supported, they make better choices—and ultimately, that leads to healthier communities. Experience the Bloom Difference If you’re tired of waiting weeks for an appointment, frustrated by confusing medical bills, or ready to experience healthcare the way it should be—personal, affordable, and convenient—Direct Primary Care may be the perfect solution. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we’re proud to offer this modern model of care that puts you first. Contact us today to learn more about how our DPC memberships work and how you can start experiencing better care for less.

As the temperatures drop and the days get shorter, we naturally start spending more time indoors — sharing space, air, and often, germs. Cold and flu season is right around the corner, and while it’s impossible to avoid every virus, you can take meaningful steps to strengthen your immune system and reduce your chances of getting sick. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we believe prevention is the best medicine. By supporting your body’s natural defenses through nutrition, hydration, rest, and wellness treatments, you can stay healthy, energetic, and resilient all season long. Here’s how to boost your immune system and stay well this fall and winter. 1. Nourish Your Body with Immune-Supporting Nutrients Your immune system needs consistent nourishment to function at its best. Eating a diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods provides the foundation for strong immune defense. Focus on foods that contain key immune-boosting vitamins and minerals such as: Vitamin C – Found in citrus fruits, bell peppers, broccoli, and strawberries, Vitamin C helps protect cells and supports white blood cell production. Vitamin D – Known as the “sunshine vitamin,” it plays a major role in immune regulation. Because sunlight exposure decreases in the fall and winter, consider supplementation or an IV Vitamin D boost. Zinc – Found in lean meats, pumpkin seeds, and legumes, zinc helps your immune cells function effectively. Probiotics – A healthy gut is essential for a strong immune system. Include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, or a daily probiotic supplement to support gut health. At Bloom, our IV Vitamin Therapy treatments deliver these vital nutrients directly into your bloodstream for maximum absorption and immediate benefits. An Immune Boost IV, rich in Vitamin C, zinc, and other key nutrients, can help your body stay strong through the changing seasons. 2. Stay Hydrated — Even When It’s Cold It’s easy to drink less water when the weather cools down, but proper hydration is just as important in fall and winter as it is in summer. Hydration keeps your mucous membranes moist — your body’s first line of defense against viruses entering through the nose and mouth. Try these hydration tips: Keep a warm herbal tea or lemon-infused water nearby throughout the day. Eat hydrating foods such as soups, fruits, and vegetables. If plain water feels unappealing, try sparkling water or add a splash of juice for flavor. For an extra boost, our Hydration IV therapy can quickly replenish fluids and electrolytes to keep your body functioning optimally, especially after illness or travel. 3. Prioritize Quality Sleep Sleep isn’t just rest — it’s your body’s time to repair, restore, and strengthen your immune response. Studies show that even mild sleep deprivation can weaken immune function, making you more susceptible to infections. To improve your sleep quality: Keep a consistent bedtime and wake-up schedule. Avoid screens and blue light 1 hour before bed. Create a relaxing bedtime routine — dim the lights, sip herbal tea, and practice deep breathing. Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. If stress or hormonal changes are keeping you up at night, Bloom can help you explore supportive treatments such as hormone balancing therapy or nutrient IVs designed to promote relaxation and restore balance. 4. Move Your Body Regularly Regular physical activity keeps your immune system active and responsive. Exercise promotes healthy circulation, reduces stress hormones, and supports the movement of immune cells throughout the body. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate movement most days of the week. That could mean a brisk walk in the crisp fall air, yoga, or strength training. However, balance is key — overtraining or pushing through exhaustion can actually suppress your immune system. Listen to your body and prioritize recovery, especially during high-stress or high-exposure times. 5. Manage Stress — Your Immune System Depends On It Chronic stress has a powerful impact on immune function. Elevated cortisol levels suppress immune activity, making it harder for your body to fight off viruses. Build in daily moments to rest and reset: Practice mindful breathing or meditation for 5–10 minutes a day. Spend time outdoors or connect with loved ones. Engage in activities that bring you joy or calm — reading, journaling, or a warm bath. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we take a whole-body approach to wellness because your mental and physical health are deeply connected. Managing stress isn’t indulgent — it’s essential to keeping your immune system resilient. 6. Consider IV Vitamin Therapy for Extra Support Sometimes, even the healthiest routines need a little reinforcement. IV Vitamin Therapy is a fast and effective way to strengthen your immune system by delivering nutrients directly into your bloodstream — bypassing the digestive system for maximum absorption. Our Immune Boost IV at Bloom Health and Wellness includes high-dose Vitamin C, zinc, and essential B vitamins to: Reduce fatigue and support recovery Enhance your body’s immune response Support healthy energy and hydration levels If you’re feeling run down, recovering from illness, or preparing for travel, IV therapy can help you bounce back quickly and maintain your wellness through the season. 7. Don’t Forget Preventive Health Visits Routine wellness visits are one of the best tools for prevention. At Bloom Health and Wellness, our Direct Primary Care (Concierge Medicine) model gives you direct access to your provider for personalized care, quick responses, and proactive prevention — not just sick visits. Fall is a great time to: Review your vitamin and hormone levels Check your thyroid and metabolic health Discuss immune-boosting treatments or supplements Get personalized recommendations to stay healthy all season With our membership-based care, you’ll enjoy same or next-day appointments, direct messaging with your provider, and no surprise bills — making preventive care simple and accessible. Stay Healthy, Stay Blooming Cold and flu season doesn’t have to mean endless tissues and sleepless nights. By supporting your immune system through good nutrition, hydration, rest, and preventive care, you can enjoy the cooler months feeling strong, vibrant, and well. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we’re here to help you build resilience from the inside out — so you can stay healthy through every season.

As summer fades and fall routines pick up, many people find themselves juggling packed schedules, shifting priorities, and new demands on their time. Back-to-school activities, upcoming holidays, shorter days, and colder weather can all combine to leave us feeling overwhelmed. The good news? Fall can also be a season of renewal and grounding. By embracing simple mind-body practices, you can reduce stress, restore balance, and head into the colder months feeling calm and centered. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we believe that supporting your mental and emotional health is just as important as caring for your physical body. Let’s explore practical ways to stay grounded and stress-free this season. Why Fall Can Feel So Stressful Seasonal transitions affect more than just the weather—they impact our bodies and minds, too. During the fall, stress levels may rise because of: Busier schedules as kids return to school or work ramps up after summer vacations. Shorter days leading to changes in mood and energy levels. Holiday anticipation bringing added responsibilities and social pressures. Less outdoor time, which can reduce natural stress relief from movement and sunlight. Recognizing these stressors is the first step in managing them. The Importance of Mind-Body Practices Mind-body practices are tools and activities that connect your physical state to your mental and emotional well-being. They help regulate stress hormones, improve your immune system, and even support better sleep and focus. When practiced regularly, these habits don’t just “manage” stress—they build resilience so you’re less affected by it in the first place. Mind-Body Practices to Stay Grounded This Fall 1. Start Your Day with a Grounding Routine Instead of diving straight into emails or your to-do list, take 5–10 minutes each morning for yourself. Stretch gently or practice light yoga. Do a quick breathing exercise to center your mind. Set an intention for the day (“I approach today with calm and clarity”). This small shift can help you feel in control no matter how busy your day gets. 2. Practice Deep Breathing or Meditation Breathwork and meditation are proven to lower cortisol (your stress hormone). Box Breathing: Inhale for 4 counts, hold for 4, exhale for 4, hold for 4. Repeat. Guided Meditation: Apps like Calm or Headspace offer 5-minute sessions perfect for busy people. Even a few minutes during a lunch break or before bed can reset your nervous system. 3. Get Outside Every Day Crisp fall air and colorful leaves can be surprisingly therapeutic. Natural light helps regulate your circadian rhythm and boosts mood. Try: Taking a 10-minute walk between tasks. Eating lunch outside. Planning a weekend hike to enjoy the season’s beauty. 4. Move Your Body Mindfully Exercise is a powerful stress-buster, but it doesn’t have to be intense. Gentle, mindful movement helps release tension without overstimulating your body. Consider: Yoga or Pilates classes. Tai chi or qigong. *Dance or simple stretching at home. These activities enhance circulation, release endorphins, and calm the nervous system simultaneously. 5. Nourish Your Body with Stress-Reducing Foods What you eat impacts how you feel. This fall, stock up on: Omega-3-rich foods (salmon, walnuts, chia seeds) to reduce inflammation and support brain health. Magnesium-rich foods (leafy greens, pumpkin seeds, dark chocolate) to promote relaxation. Herbal teas (chamomile, lemon balm) to soothe your nervous system. Hydration matters, too—dehydration can amplify feelings of stress and fatigue. Bloom Health and Wellness Can Support Your Stress-Relief Journe y Sometimes lifestyle changes aren’t enough on their own. That’s where personalized care can help. At **Bloom Health and Wellness**, we offer: IV Vitamin Therapy to replenish nutrients depleted by stress, like B vitamins and magnesium. Bioidentical Hormone Therapy to balance mood, energy, and sleep if hormonal changes are contributing to stress. Direct Primary Care Memberships for consistent, personalized support without the hassle of traditional healthcare. These services complement your self-care efforts and help your body handle stress more effectively. Make Stress Management a Seasonal Habit Stress relief isn’t just something you do once in a while—it’s an ongoing practice. By building small, consistent habits this fall, you’ll not only feel calmer now but also build resilience for the busy holiday season ahead. Final Thoughts Fall is a beautiful season of transition. With the right tools, it can also be a time of grounding and growth. Whether it’s a few minutes of mindful breathing, a warm cup of tea, or a nutrient boost with IV therapy, every small step you take to support your mind and body adds up. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we’re here to help you feel your best—inside and out. Together, we can create a plan to keep you calm, energized, and thriving through every season.

As the carefree days of summer fade into the crisp mornings of September, many of us start thinking about the months ahead. School is back in session, schedules get busier, and cooler weather means we’re spending more time indoors—perfect conditions for colds and flu to start circulating. The good news? There’s a lot you can do now to strengthen your immune system before the season hits full force. By making small, intentional changes to your daily routine and supporting your body with the right nutrients, you can give yourself the best chance of staying healthy all fall and winter long. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we believe prevention is the best medicine. Let’s explore some proven strategies to support your immune health. Why Focus on Immunity in the Fall? Your immune system is your body’s natural defense against viruses and bacteria. During fall and winter, it often works overtime because: Increased exposure: Kids bring germs home from school, and adults encounter more people indoors. Dryer air: Heaters and cooler weather dry out nasal passages, making it easier for viruses to spread. Less sunlight: Reduced sun exposure can lead to lower Vitamin D levels, which are essential for immune function. Taking steps now helps your body respond more effectively when it’s challenged by seasonal illnesses. Everyday Habits That Strengthen Immunity 1. Prioritize Restful Sleep Your immune system needs sleep to recharge. Adults should aim for 7–9 hours each night. Poor or interrupted sleep weakens immune defenses and makes you more vulnerable to colds. Create a consistent bedtime routine. Limit screens before bed. Keep your bedroom cool and dark for better rest. 2. Eat Nutrient-Rich Foods Food is one of the most powerful tools for immune health. Focus on: Vitamin C: Citrus fruits, bell peppers, and broccoli. Zinc: Pumpkin seeds, beans, and lean meats. Antioxidants: Colorful fruits and vegetables fight free radicals and support cell health. Protein: Vital for producing immune cells. 3. Stay Hydrated Water helps carry nutrients throughout your body and flush out toxins. Aim for at least 8 cups daily—and don’t forget warm teas with ginger or turmeric, which have added anti-inflammatory properties. 4. Move Your Body Moderate, regular exercise improves circulation and strengthens immune response. Think daily walks, yoga, or light strength training—just enough to get your blood flowing. 5. Manage Stress Stress hormones like cortisol can suppress immune function. Incorporating mindfulness practices such as deep breathing, meditation, or journaling can go a long way in keeping stress under control. The Role of Nutrients and Supplements Even with a healthy lifestyle, it can be challenging to get optimal amounts of immune-supportive nutrients through diet alone. Key supplements include: Vitamin D: Essential for immune regulation, often low during fall and winter. Vitamin C: Reduces the duration and severity of colds. Zinc: Helps immune cells function properly. Probiotics: Support gut health, which is closely tied to immunity. How IV Vitamin Therapy Can Help One of the fastest and most effective ways to boost your immune system is through **IV vitamin therapy**. Unlike oral supplements, IV therapy delivers vitamins, minerals, and hydration directly into your bloodstream for maximum absorption. At Bloom Health and Wellness, our immune-boosting IV blends can include: High-dose Vitamin C to fight oxidative stress. B vitamins to support energy production. Zinc and magnesium for cellular health. Fluids to keep you hydrated and refreshed. Many clients find that a monthly IV session helps them stay healthier through cold and flu season, recover more quickly if they do catch something, and maintain energy even during busy fall schedules. When to Start Supporting Your Immunity The best time to strengthen your immune system is *before* you get sick. Think of it like preparing your home before a storm—when your defenses are ready, you weather the challenges more easily. Starting in September gives your body a chance to build resilience ahead of peak cold and flu months. Final Thoughts This fall, don’t wait until you’re already under the weather to think about your immune health. By prioritizing rest, nutrition, hydration, movement, and stress management—and adding in extra support like supplements or IV vitamin therapy—you can give your body the tools it needs to stay strong. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we’re here to support you in building a healthier, more resilient you. Whether it’s through lifestyle guidance, personalized care, or immune-boosting IV treatments, we’re committed to helping you thrive through every season.

There’s something about late summer that feels like a fresh start. Maybe it’s the smell of new notebooks, the sight of sharpened pencils, or the return of structured routines as kids head back to school. Even if you’re not packing lunches or waiting in the car line, the “back-to-school” season offers a natural opportunity to pause, refocus, and realign your personal goals. Just like January’s “New Year” energy, August and September can bring their own sense of renewal—without the holiday chaos and cold weather. Whether you’re looking to improve your health, boost your energy, or start a new project, this is the perfect time to lay the groundwork for success. Why the Back-to-School Season Works for Goal-Setting 1. A Return to Routine Summer often means flexible schedules, travel, and a more relaxed pace. While that’s great for recharging, it can also throw healthy habits off track. The return of the school calendar—whether for you, your family, or just your community—naturally reintroduces structure. This makes it easier to plan workouts, meal prep, or consistent self-care practices. 2. Seasonal Energy Shift As the days begin to cool and the pace of life settles into a more predictable rhythm, our brains are primed for focus. Psychologists call this the “fresh start effect”—a mental boost that comes from tying new goals to meaningful time markers, like the start of a school year. 3. A Chance to Reset Before the Holidays By starting now, you can establish solid routines before the busy (and often indulgent) holiday season. Small, steady changes in September can mean you’re already in a healthy groove by November. Healthy Habits to Build This Season If you’re ready to take advantage of this “fresh start” energy, here are a few habits to consider: Prioritize Sleep Just like students need rest to learn and focus, adults need adequate sleep for productivity, mood, and health. Aim for 7–9 hours a night and keep a consistent bedtime. Schedule Movement Treat workouts like important appointments—put them in your calendar and honor them. Even a brisk 20-minute walk daily can make a difference. Meal Plan with Purpose Packing lunches isn’t just for kids! Planning healthy meals and snacks for the week reduces impulse choices and supports better nutrition. Limit Screen Time Before Bed Blue light can disrupt your sleep cycle. Try a tech curfew an hour before bed to help your mind and body wind down. Practice Mindful Mornings Start the day with 5–10 minutes of intentional quiet—whether through meditation, journaling, or deep breathing—to set a positive tone. Setting Goals That Stick The key to lasting change is to set SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Instead of saying, “I want to be healthier,” try, “I will walk 30 minutes, 5 days a week, for the next month.” Also, start small. Choose 1–2 habits to focus on instead of trying to overhaul everything at once. Progress is easier to maintain when you’re not overwhelming yourself. Make This Your Season of Growth Whether you have children in school or not, embrace this time of year as your personal “reset button.” The routines and energy of the back-to-school season are a powerful springboard for creating habits that will carry you through the rest of the year—and beyond. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we’re here to help you reach your goals and feel your best year-round. From personalized health plans to supportive treatments, our team is ready to guide you every step of the way.
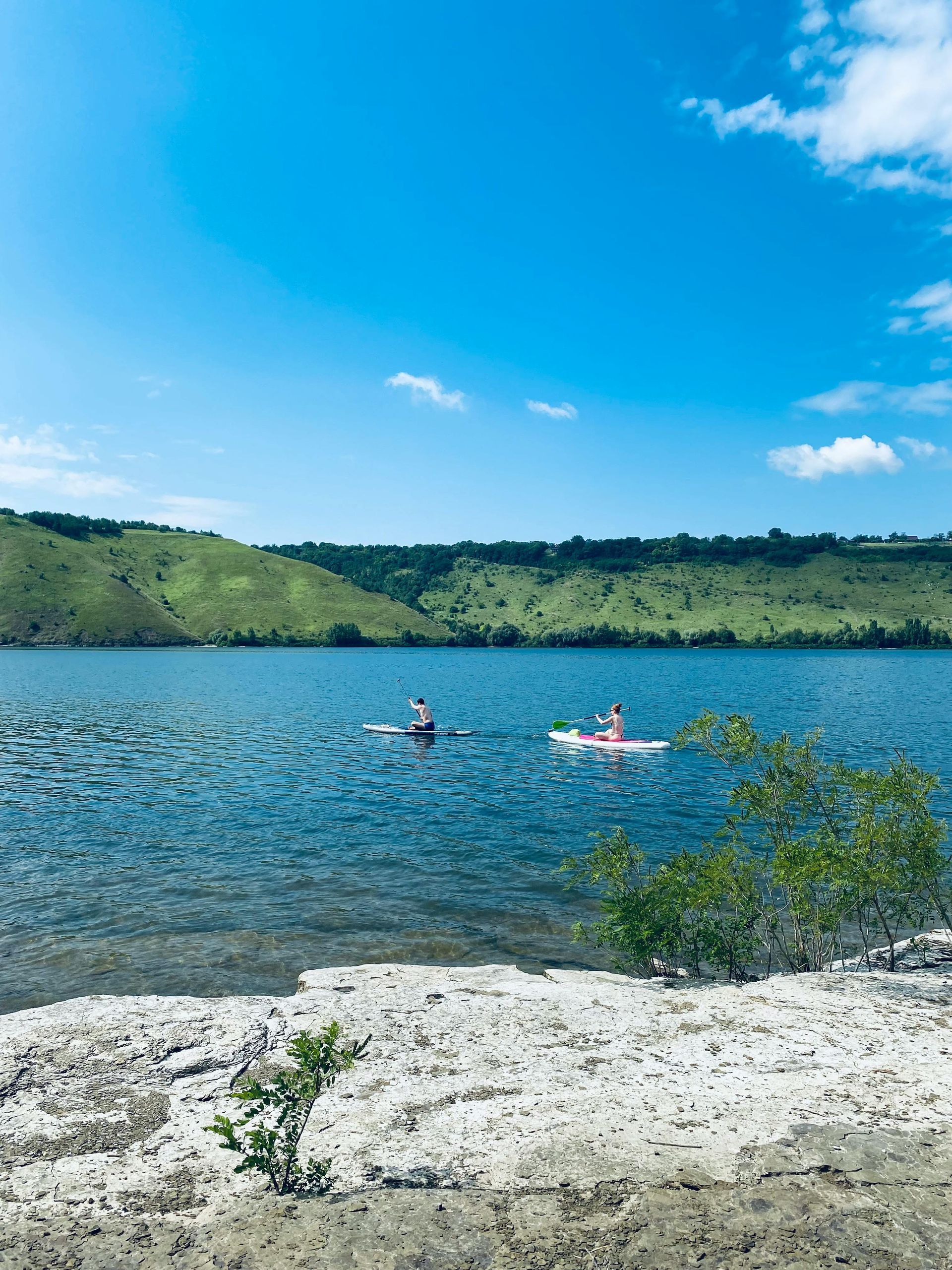

Summer brings sunshine, vacations, backyard barbecues, and longer days perfect for soaking up the outdoors. But it also brings soaring temperatures, increased humidity, and a few health challenges that are easy to overlook—especially when we're focused on fun in the sun. Wnjoying the season doesn’t have to come at the expense of your health. With the right strategies in place, you can thrive all summer long—staying energized, hydrated, and protected. Here’s your ultimate guide to Summer Wellness Essentials, including key tips on hydration, sun protection, boosting energy levels, and keeping your body balanced through the hottest months of the year. 1. Hydration: Your #1 Summer Priority As temperatures rise, your body works harder to cool itself. That means increased sweating—and increased risk of dehydration. Why Hydration Matters More in Summer: * Dehydration can lead to fatigue, headaches, brain fog, dizziness, and even heat exhaustion. * Sweating causes loss of not just water, but also **essential electrolytes** like sodium, potassium, and magnesium. * Even mild dehydration can impact energy levels, digestion, and mood. Hydration Tips: ✅ Drink more than you think you need – Aim for at least 8–10 cups of water per day, and more if you're active or spending time in the heat. ✅ Electrolytes are essential – Use electrolyte powders or natural sources like coconut water, or consider **IV hydration therapy** to quickly restore balance. ✅ Watch the signs – Thirst, dry mouth, dark urine, fatigue, and lightheadedness are signs you may already be dehydrated. ✅ Carry a water bottle everywhere – Make it easy to sip throughout the day. Pro Tip: Try infusing water with cucumber, lemon, or mint for a refreshing twist that also supports digestion and cooling. 2. Sun Protection: Guard Your Skin and Health A little sunshine helps your body make vitamin D, but too much unprotected exposure can lead to premature aging, sunburn, and increased risk of skin cancer. Why UV Protection Is Crucial: UV rays are strongest between 10am–4pm, and even cloudy days don’t block all the damage. Cumulative sun exposure can cause dark spots, fine lines, and skin texture changes. Overexposure can deplete **glutathione**, a key antioxidant that protects your cells from damage. Sun Protection Tips: ☀️ Apply SPF 30+ daily – Even if you’re not heading to the beach, your skin is still exposed on walks, drives, and errands. ☀️ Reapply every 2 hours – Especially if you’re sweating or swimming. ☀️ Protective clothing and hats – Long sleeves, wide-brim hats, and sunglasses can help block UV rays without relying on products alone. ☀️ Seek shade – Try to limit direct exposure during peak UV hours. Bonus Support: Consider antioxidant-rich supplements like vitamin C, glutathione, and zinc, which help protect skin from the inside out. At Bloom, we offer IV nutrient therapy to help support your skin’s resilience and radiance all summer long. 3. Maintain Energy and Beat the Heat Fatigue Ever feel like the heat just drains you? That’s because high temperatures place extra demands on your cardiovascular system and deplete your body’s resources—especially if you’re not properly fueled or rested. Causes of Low Energy in Summer: Dehydration Poor sleep (from longer daylight or warmer nights) Blood sugar fluctuations from irregular eating Mineral depletion from sweating Hormonal or thyroid imbalances made worse by seasonal shifts Energy-Boosting Tips: ⚡ Eat light, nutrient-dense meals – Focus on fresh produce, lean protein, and complex carbs to fuel your body without weighing it down. ⚡ Don’t skip meals – Long gaps between meals can lead to blood sugar crashes and afternoon fatigue. ⚡ Get outside early or late – Morning sunlight can improve your circadian rhythm and boost vitamin D naturally. ⚡ Try B12 and MIC injections – These can support metabolism, energy production, and mental clarity. 4. Summer-Friendly Nutrition for Optimal Wellness Summer is full of seasonal produce that not only tastes amazing but also supports hydration, digestion, and cellular health. Eat More of These Summer Superfoods: 🍉 Watermelon – Packed with water, electrolytes, and lycopene (a skin-protective antioxidant). 🥒 Cucumbers – Refreshing and hydrating with anti-inflammatory properties. 🍓 Berries – Rich in antioxidants to fight oxidative stress and sun damage. 🌽 Corn – Contains lutein and zeaxanthin, which support eye health under bright sun exposure. 🍅 Tomatoes – Full of vitamin C and lycopene for skin and immune health. 🥗 Leafy greens – Help balance fluids and provide magnesium for muscle and nerve function. Keep Meals Light but Satisfying: Grill lean proteins like chicken, salmon, or tofu. Make chilled grain bowls with quinoa, chopped veggies, and avocado. Snack smart with Greek yogurt, hard-boiled eggs, or raw nuts. And don’t forget to limit sugary drinks and alcohol , which contribute to dehydration and energy crashes. 5. Keep Your Body Moving—Safely Staying active in the summer has incredible benefits, from mood-boosting endorphins to improved metabolism and heart health. But it’s important to adjust your routine to avoid overheating or exhaustion. Smart Summer Fitness Tips: 🏃♀️ Exercise early or late – Avoid peak heat by moving in the early morning or after sunset. 🏖️ Take it outside – Try swimming, paddleboarding, hiking, or beach yoga to keep movement fun. 💧 Hydrate before, during, and after – Don’t wait until you feel thirsty. 🧘 Listen to your body – Take breaks, cool down, and don’t push through heat exhaustion. If you’re new to working out or returning after a break, start small—consistency matters more than intensity. Even a daily 20-minute walk can boost your mood, metabolism, and circulation. 6. Prioritize Quality Sleep—Even in the Heat Longer daylight and warmer nights can disrupt your sleep—yet rest is essential for hormone balance, weight control, and immune health. Tips for Better Summer Sleep: 🌙 Darken your room – Use blackout curtains to block evening light and promote melatonin production. 🌡️ Cool your space – Use fans, AC, or breathable bedding to avoid overheating at night. 📵 Power down earlier – Avoid screens before bed to help your body wind down. 📆 Keep a consistent routine – Even on weekends or vacations, try to go to bed and wake up at the same time. Poor sleep can worsen stress, appetite, and mood—so don’t underestimate its impact. If you struggle to sleep, talk to us about testing your cortisol, melatonin, or thyroid levels, all of which affect rest and recovery. 7. Protect Your Immune System We often associate colds and flu with winter, but summer brings its own immune stressors—from travel and disrupted routines to increased exposure at events and gatherings. Summer Immune Support Tips: 🛡️ Stay hydrated to support detoxification 🛡️ Eat a rainbow of fruits and veggies to boost antioxidant levels 🛡️ Get enough sleep for immune cell repair 🛡️ Supplement as needed with vitamin C, D, and zinc 🛡️ Consider IV therapy before travel or big events to support your defenses If you find yourself getting run-down or sick more often in summer, it could be a sign of underlying stress, inflammation, or nutrient depletion. We can help assess and support your immune system year-round. 8. Use Summer to Reconnect With Your Health Goals Summer is a great time to check in with your overall wellness—not just physically, but mentally and emotionally too. ☀️ Are you managing stress in healthy ways? ☀️ Are your hormones balanced? ☀️ Do you feel confident in your skin? ☀️ Are you on track with your long-term goals? Sometimes, feeling “off” in summer isn’t just about the heat—it can be the result of hormonal shifts, thyroid dysfunction, or metabolic imbalances. Final Thoughts: Summer Is Better When You Feel Your Best With a little intention and the right support, you can enjoy all that summer has to offer—without sacrificing your health or well-being. Summer Wellness Essentials aren’t about restriction or perfection. They’re about giving your body what it needs to feel energized, nourished, protected, and balanced—so you can make the most of this vibrant season.

As the warm days of summer settle in and the year hits its halfway mark, July presents a powerful opportunity to pause, reflect, and realign with your health and wellness goals. Whether you started the year with ambitious resolutions or simply hoped to make better daily choices, now is the perfect time to check in with yourself and make meaningful progress in the months ahead. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we believe that transformation happens not in big, dramatic moves, but through small, consistent actions. A mid-year reset isn’t about guilt or perfection—it’s about recommitting to the version of yourself you want to become, and setting up the systems to get there. Here’s how to assess where you are, clarify where you’re going, and reignite your motivation to feel your best for the rest of the year. 1. Reflect on the First Half of the Year Before you can move forward, it’s important to look back. What were your goals at the beginning of the year? Maybe you wanted to lose weight, exercise more, sleep better, reduce stress, or simply feel healthier overall. Ask yourself: What went well? What didn’t go as planned? What habits supported your health? What patterns held you back? Be honest, but gentle. Reflection isn’t about criticism—it’s about gathering data. For example, maybe you noticed that you exercised consistently when you had accountability, or that you struggled with energy levels in the afternoon. These are clues that can help shape a more realistic and effective plan going forward. Tip: Take 15–20 minutes to journal or jot down your observations. This is a powerful way to get clarity and reset your focus. 2. Reevaluate Your Health Goals As life shifts, so do your priorities. What felt important in January may not align with your needs today—and that’s okay. Now is the time to ask: Are my goals still relevant? Do they reflect my current lifestyle and values? Do they excite and motivate me? If you set vague goals like “get healthier” or “lose weight,” try redefining them using the SMART framework: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For instance, rather than “lose weight,” your updated goal might be: “Lose 10 pounds by September by walking 5 days a week and reducing added sugars.” 3. Audit Your Daily Habits Big goals are built on small actions. Once you’ve clarified your priorities, take a close look at your daily routines. Are your current habits helping or hindering your progress? Consider: What does your morning routine look like? How consistent is your meal planning or hydration? Are you making time for movement or self-care? Are you getting quality sleep? Small tweaks—like going to bed 30 minutes earlier, prepping lunches ahead of time, or scheduling your workouts—can make a big difference over time. Pro tip: Focus on one to three key habits to improve rather than trying to overhaul your entire routine. Sustainable change is built slowly and steadily. 4. Get Support Where You Need It If you’ve been trying to make changes on your own and feel stuck, you’re not alone. One of the biggest reasons people fall off track is lack of support and accountability. This is where a wellness provider or health coach can make all the difference. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we offer: Weight loss programs tailored to your unique body and goals Direct Primary Care memberships for convenient, ongoing support Hormone and thyroid evaluations to uncover hidden imbalances IV nutrition and vitamin injections to help boost energy and overall vitality We meet you where you are and provide guidance that fits into your real life—not a cookie-cutter plan that leaves you frustrated or overwhelmed. 5. Optimize Your Energy and Focus Summer often brings schedule disruptions, late nights, and more indulgences. If you’re feeling sluggish, scattered, or just “off,” your body may be telling you it needs some extra support. Here are a few health factors to consider during your mid-year reset: Hydration: Are you drinking enough water—especially in the heat? Sleep: Are you getting restful sleep, or waking up feeling tired? Stress: Are you managing stress in healthy ways or just pushing through? Nutrition: Are you fueling your body with balanced meals? Micronutrients: Are you possibly low in key vitamins like B12, D, or magnesium? If any of these areas feel off, it's worth addressing them. In fact, many patients we work with find that low energy or poor focus is linked to underlying issues like hormone imbalance, nutrient deficiencies, or blood sugar dysregulation—all of which can be tested and treated. 6. Don’t Wait for “Perfect”—Start Now One of the biggest mid-year traps is the belief that since the first half of the year didn’t go perfectly, the rest of the year is already lost. This couldn’t be further from the truth. Here’s a simple mindset shift: It’s not too late. It’s right on time. Summer is actually an ideal season to get back on track: Longer daylight hours can encourage outdoor activity. Fresh seasonal produce makes healthy eating easier. A more relaxed vibe allows time for reflection and planning. Even if you start with just one action—like walking daily or cutting out soda—you’re building momentum. That’s how real change begins. 7. Rebuild Motivation with Micro-Wins Motivation isn’t something you either have or don’t—it’s something you build. One of the most effective ways to stay motivated is to create small wins that reinforce your progress. Celebrate little victories like: Drinking 64 oz. of water every day for a week Cooking three healthy meals at home Choosing to walk instead of drive for a short errand Saying no to something that drains your energy These small moments add up to big results, and they help keep you focused when the initial excitement wears off. Remember, progress is progress—no matter how small. 8. Recommit to Long-Term Wellness Health is not a 30-day challenge—it’s a lifelong relationship with your body and mind. A mid-year reset is the perfect chance to recommit to the long game. This might include: Getting lab work done to understand your baseline Scheduling regular follow-ups with your provider Investing in memberships or programs that keep you accountable Developing mental health habits like meditation, gratitude, or journaling Long-term wellness is about creating systems that support you. At Bloom Health and Wellness, we’re here to help you build those systems—with compassion, expert care, and a whole-person approach that works. 9. Set a Vision for December 2025 It might feel far off, but think ahead: When this year wraps up, how do you want to feel? Imagine it’s the end of December. Would you like to: Feel stronger and more energized? Have better sleep and fewer aches and pains? Feel more confident in your clothes? Know that you took control of your health? Let that vision guide your decisions now. Write it down. Revisit it when you lose steam. Your future self will thank you for every healthy choice you make today. Final Thoughts: A Fresh Start Begins Now You don’t need a new year to make a new commitment. July is your fresh start. It’s your permission to regroup, recharge, and reignite your passion for health and wellness. If you’re ready to take the next step, we’re here to walk beside you. Whether you need support with weight loss, hormones, nutrition, or simply feeling your best—Bloom Health and Wellness offers the guidance, tools, and personalized care to help you thrive. Let’s make the second half of the year your healthiest yet.
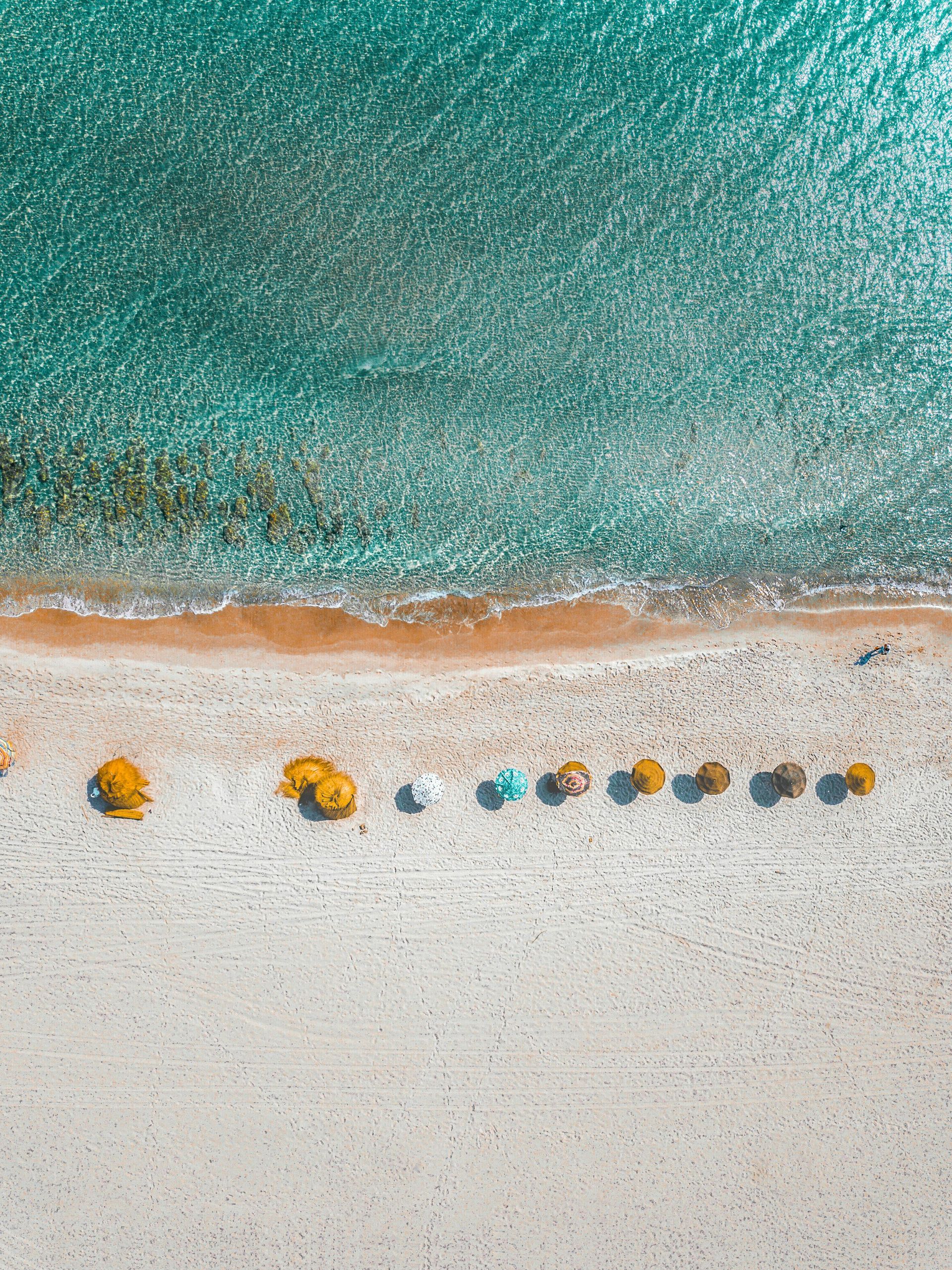

Summer is a season of sunshine, vacations, outdoor adventures—and often, disrupted routines. Between kids being out of school, long-awaited trips, and more social events than usual, it can be easy to let your healthy habits slip. But just because your schedule changes doesn't mean your wellness has to take a back seat. Here’s how you can enjoy everything summer has to offer while staying aligned with your health goals: 1. Reframe Your Routine—Not Abandon It Your usual structure might look different in the summer, but that doesn't mean all healthy habits have to go out the window. Adapt rather than abandon. For example: If your morning workout is no longer realistic, try an evening walk after dinner. If travel disrupts your meal prep, plan a few easy-to-pack snacks or research healthy restaurant options ahead of time. If your kids are home from school, involve them in activities like bike rides, outdoor games, or cooking nutritious meals together. Think of your routine as flexible, not fragile. 2. Prioritize Hydration Hotter temperatures and increased activity make staying hydrated more important than ever. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, headaches, and even sugar cravings. Aim to: Carry a reusable water bottle with you throughout the day. Add fruit or herbs (like lemon, cucumber, or mint) to your water for flavor. Opt for hydrating foods like watermelon, berries, cucumbers, and leafy greens. Set phone reminders if needed—staying hydrated is one of the simplest ways to feel better all day long. 3. Keep Nutrition Simple and Seasonal Summer is the perfect time to enjoy fresh, seasonal produce. Local farmers markets are full of vibrant fruits and vegetables that make it easier (and tastier) to eat well. Grill veggies and lean proteins for quick, healthy meals. Blend up smoothies with summer fruits, leafy greens, and a scoop of protein or collagen powder. Watch out for hidden sugar in summer treats—enjoy in moderation and savor every bite. Remember, healthy eating doesn’t mean restriction—it means being intentional. 4. Make Movement Part of the Fun You don’t need a gym to stay active. Summer offers natural opportunities for movement: Go swimming, paddleboarding, or hiking. Take a walk at sunset to avoid the hottest part of the day. Start a friendly step-count challenge with your family or coworkers. Staying active helps with energy, mood, and metabolism—even if your workout doesn’t look like your usual routine. 5. Be Mindful on Vacation Vacations are meant to be enjoyed—but they don’t have to mean a total detour from your wellness goals. A few tips: Bring resistance bands or a yoga mat to do quick workouts in your hotel or rental. Stick to your sleep routine as much as possible—your body thrives on rhythm. Indulge mindfully: enjoy your favorite foods, but pause and ask yourself what your body really needs, too. Balance is the goal, not perfection. 6. Stay Connected to Your “Why” Summer distractions can make it easy to lose sight of your health goals. Reconnect with the reason behind your habits: Do you want more energy to enjoy time with your family? Are you working on managing a health condition? Are you committed to long-term wellness? Whatever your “why” is, keep it front and center—it’s your compass when things feel off track. 7. Give Yourself Grace and Keep Going One off day—or even a whole week—doesn’t undo all your progress. If you find yourself slipping, don’t beat yourself up. Instead: Reflect on what pulled you off track. Recommit to one small habit you can restart today. Celebrate the wins, no matter how small. Consistency matters more than perfection. Final Thoughts Summer is a time to enjoy life—and that includes caring for your health in a way that supports the season you’re in. With a few smart adjustments, you can stay on track with your healthy habits and return to fall feeling energized, balanced, and proud of your efforts. Need help maintaining your wellness goals this summer? At Bloom Health and Wellness, we offer personalized guidance, support, and treatments—from nutrition counseling to IV therapy—to help you feel your best all year long. Let this summer be one of vitality, joy, and whole-body health.
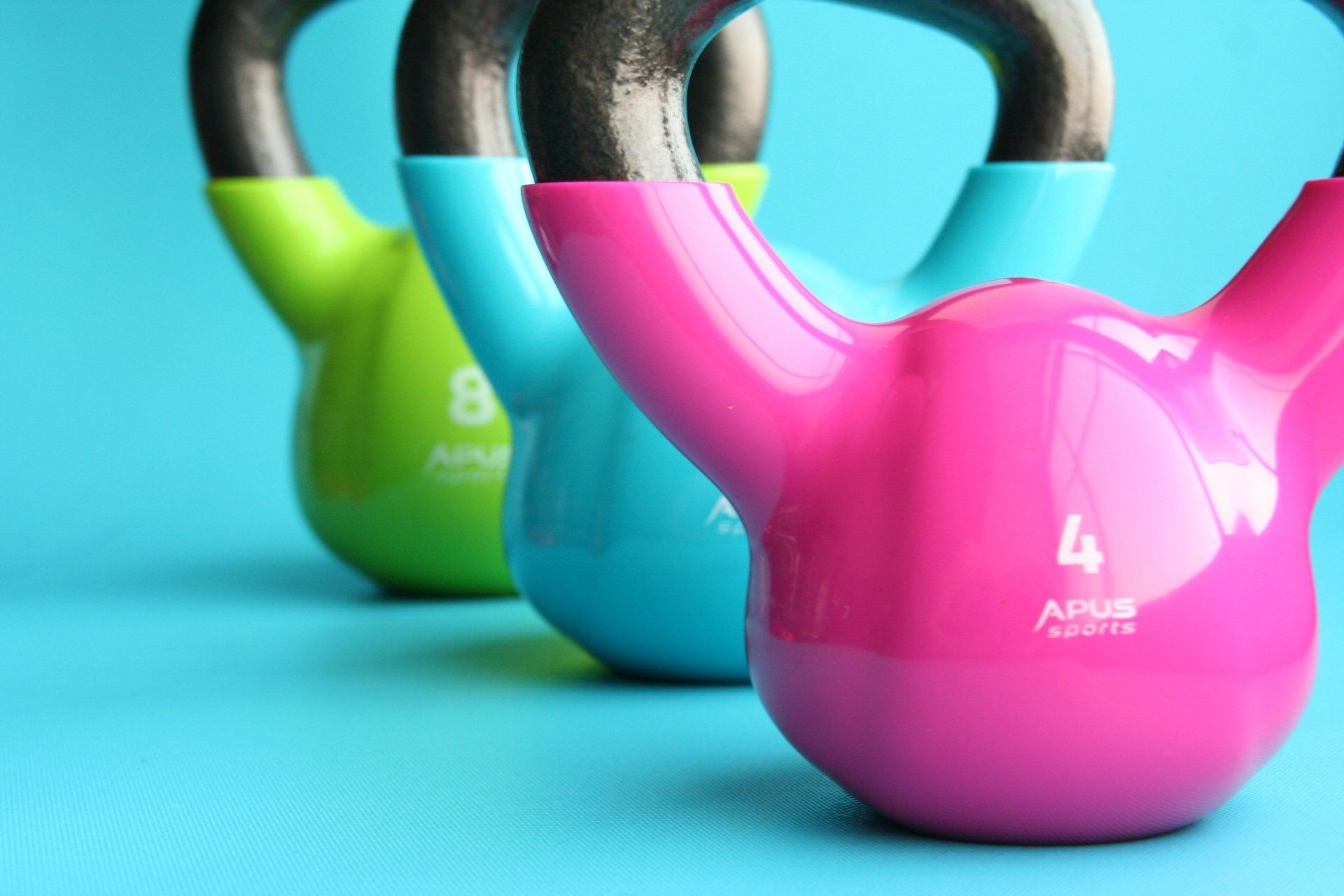

When it comes to improving health and shedding excess weight, most people think of cardio, diet plans, or the latest fitness trend. But one crucial—and often overlooked—component of sustainable health is **strength training**. Whether you're looking to lose weight, age gracefully, or support your body while using medications like GLP-1 receptor agonists (e.g., semaglutide), strength training offers unparalleled benefits. The Foundation of Strength Training Strength training, also known as resistance training or weight lifting, involves working your muscles against resistance to build strength, endurance, and muscle mass. This can include bodyweight exercises, resistance bands, dumbbells, kettlebells, or weight machines. Benefits of Strength Training for Overall Health Strength training isn’t just for athletes or bodybuilders. It’s a critical part of a healthy lifestyle for everyone—regardless of age or fitness level. Here’s why: 1. Increased Muscle Mass and Metabolism Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue. The more lean muscle you have, the higher your resting metabolic rate. This means you burn more calories throughout the day—even when you’re not exercising. 2. Improved Bone Density Weight-bearing exercises help stimulate bone growth and reduce the risk of osteoporosis, which becomes especially important as we age. 3. Better Balance and Mobility Strong muscles contribute to better balance, coordination, and posture. This helps prevent falls and injuries, especially in older adults. 4. Blood Sugar and Heart Health Benefits Strength training improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate blood sugar, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and improving cardiovascular health. 5. Mental Health Boost Resistance training has been linked to reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression, increased confidence, and better overall mental well-being. Strength Training and Weight Loss: The Missing Link Many people focus on cardio and cutting calories when trying to lose weight—but strength training is essential for fat loss and body composition improvements. When you lose weight through diet alone, you typically lose a mix of fat and muscle. Strength training helps you preserve—and even build—lean muscle mass during a calorie deficit, which is key for: Keeping your metabolism high Improving how your body looks and feels (i.e., more “toned”) Preventing weight regain once your diet ends And here’s the best part: the afterburn effect. Post-workout, your body continues to burn calories for hours after strength training as it repairs and rebuilds muscle tissue. Why Strength Training is Crucial if You're Taking a GLP-1 Medication GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) or tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Zepbound) are powerful tools for weight loss. They reduce appetite, improve blood sugar control, and help people lose a significant amount of weight. However, not all that weight loss is fat—a portion of it may be lean muscle mass, especially without proper nutrition and physical activity. Here’s why adding strength training is non-negotiable if you're using a GLP-1 medication: 1. Preserve Lean Muscle Mass GLP-1s help you eat less, but reduced caloric intake can lead to muscle loss if you’re not strength training. Losing muscle can slow your metabolism and make it harder to maintain weight loss long term. 2. Maintain Functional Strength Rapid weight loss may leave some people feeling weaker or more fatigued. Regular strength training helps maintain physical strength, energy levels, and overall vitality. 3. Support Long-Term Results Medications can help you lose weight—but maintaining that loss depends on creating a strong, healthy foundation. Strength training supports a healthy metabolism and helps prevent the “yo-yo” effect many people experience after weight loss. 4. Improve Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Health Since GLP-1s also support metabolic health, strength training complements their effects by improving glucose uptake in the muscles and lowering insulin resistance. Getting Started with Strength Training You don’t need a gym membership or fancy equipment to start reaping the benefits of strength training. Here are a few beginner-friendly tips: Start with bodyweight exercises like squats, push-ups, lunges, and planks. Aim for 2–3 sessions per week, focusing on full-body movements. Progress slowly by increasing resistance, reps, or sets as you get stronger. Consider working with a trainer if you're new to strength training or want a personalized plan. And remember: consistency is more important than intensity when you're starting out. The goal is to build a sustainable routine that supports your health for the long haul. Final Thoughts Whether your goal is to lose weight, age gracefully, or stay strong while on a weight loss medication, strength training is one of the most powerful tools at your disposal. It protects your muscle mass, boosts metabolism, and contributes to a healthier, more resilient body. If you're currently taking or considering a GLP-1 medication for weight loss, adding strength training to your routine is especially important. It can mean the difference between temporary weight loss and long-lasting health transformation. Need help getting started? At Bloom Health and Wellness, we’re here to support your journey every step of the way—from personalized wellness plans to accountability and coaching. Let’s build a stronger, healthier you—inside and out.

Spring is a season of renewal—a time when nature bursts into life, days grow longer, and the air feels fresher. However, for many, the transition from winter to spring can bring unexpected fatigue. If you find yourself struggling with energy slumps despite the season’s promise of vibrancy, you’re not alone. The good news is that you can revitalize your energy naturally by focusing on key wellness strategies such as nutrition, hydration, hormone balance, and IV vitamin therapy. Understanding Spring Fatigue While the increased daylight and warmth of spring can be uplifting, seasonal transitions can also challenge the body. Factors such as lingering winter sluggishness, disrupted sleep patterns, and the body's natural adjustments to longer days can contribute to spring fatigue. Common symptoms include: Persistent tiredness, even after a full night’s sleep Brain fog or difficulty concentrating Increased cravings for sugary or processed foods Mood fluctuations or irritability If this sounds familiar, it’s time to embrace simple yet effective natural solutions to restore your energy levels and fully enjoy the season. 1. Optimize Your Nutrition for Sustained Energy What you eat plays a critical role in determining how energized you feel throughout the day. Fueling your body with the right nutrients can prevent energy crashes and keep you feeling vibrant. Focus on Whole, Nutrient-Dense Foods Incorporate fresh, seasonal produce such as leafy greens, asparagus, berries, and citrus fruits, which provide essential vitamins and antioxidants. Prioritize lean proteins like chicken, fish, eggs, and plant-based sources like lentils and beans to maintain steady blood sugar levels.- Include healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil to support brain function and energy production. Balance Blood Sugar Fluctuating blood sugar levels are a leading cause of energy slumps. Avoid processed sugars and refined carbs, which cause rapid spikes and crashes. Instead, choose complex carbohydrates like sweet potatoes, quinoa, and whole grains that provide sustained energy. Don’t Skip Breakfast Start your day with a protein-rich breakfast to stabilize energy levels. Eggs with vegetables, a smoothie with protein powder, or Greek yogurt with nuts and berries can set the tone for a productive day. 2. Hydration: The Simple Yet Overlooked Energy Booster Even mild dehydration can lead to fatigue, headaches, and poor concentration. As temperatures rise in spring, staying adequately hydrated becomes even more important. How to Stay Hydrated: Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day, or more if you’re active. Incorporate hydrating foods such as cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges into your diet. Drink herbal teas or coconut water for added hydration and electrolytes. Limit caffeine and alcohol, which can contribute to dehydration and energy crashes. If you often forget to drink water, set reminders or carry a reusable water bottle with you throughout the day. 3. Balance Your Hormones for Consistent Vitality Hormones play a crucial role in regulating energy levels, and imbalances can lead to persistent fatigue, mood swings, and difficulty maintaining focus. Key Hormones That Impact Energy: Cortisol: The stress hormone, which, when elevated for extended periods, can lead to adrenal fatigue and low energy. Thyroid Hormones: An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can cause sluggishness and slow metabolism. Insulin: Poor insulin regulation can result in blood sugar crashes and energy dips. Estrogen & Testosterone: Imbalances in these hormones can affect both men and women, leading to fatigue, brain fog, and muscle weakness. How to Support Hormone Balance Naturally: Manage Stress: Chronic stress can deplete energy. Practice mindfulness, deep breathing, or yoga to keep cortisol in check. Prioritize Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of high-quality sleep each night, and maintain a consistent sleep schedule. Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps regulate hormones, improve circulation, and boost energy levels. Consider Hormone Testing: If you suspect hormonal imbalances, consulting with a healthcare provider for testing and bioidentical hormone therapy may help restore balance. 4. Harness the Benefits of IV Vitamin Therapy If you’re struggling with low energy despite maintaining good habits, IV vitamin therapy can be a game-changer. This treatment delivers essential vitamins, minerals, and hydration directly into your bloodstream for maximum absorption. How IV Therapy Boosts Energy: Replenishes Nutrient Deficiencies: Many people are low in key energy-boosting vitamins such as B12, magnesium, and vitamin C. Improves Hydration: IV fluids restore optimal hydration levels, helping you feel more refreshed and alert. Enhances Cellular Function: Nutrients like amino acids and antioxidants support mitochondrial function, the powerhouse of energy production in your cells. Popular IV blends for energy include high-dose vitamin C, B-complex vitamins, and amino acids to revitalize your body and mind. 5. Take Advantage of Longer Days and Increased Sunlight One of the best natural energy boosters of spring is sunlight. Exposure to natural light helps regulate your circadian rhythm, improve mood, and increase vitamin D levels, all of which contribute to higher energy levels. Tips for Maximizing Sunlight Exposure: Spend at least 15-30 minutes outdoors in the morning to help reset your internal clock. Take daily walks, practice yoga in the park, or garden in natural sunlight. Open your curtains early to let natural light into your home. Consider a vitamin D supplement if you spend limited time outdoors or live in a cloudy region. Final Thoughts: Spring Into Energy Spring is a time of renewal, and by making intentional choices, you can harness the season’s natural energy to feel your best. By optimizing your nutrition, staying hydrated, balancing your hormones, considering IV vitamin therapy, and embracing the benefits of longer daylight, you can overcome fatigue and enjoy a more energized, productive season. If you’re ready to take control of your energy levels, Bloom Health and Wellness offers expert guidance, personalized treatments, and IV vitamin therapy to support your journey. Contact us today to revitalize your health and embrace the vibrancy of spring!


